How Do Bed Bugs Reproduce? [Explained In Stages]

Have you ever wondered how bed bugs reproduce and grow? You can find bed bugs in many homes across the United States. They are also found on airplanes and cruise ships, where people often don’t know that they are there. If you have had a case of bed bugs, you may be wondering what happens after they bite you.
Well, wonder no more! In this blog post, we’ll explore the life cycle of bed bugs and how they multiply.
Bed bugs reproduce and grow through a process known as incomplete metamorphosis. Female bed bugs lay small, white eggs that hatch into nymphs. The nymphs will then molt and shed their skin multiple times as they grow into adulthood. The growth process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months depending on the temperature, humidity, and availability of food.
The Life Cycle of Bed Bugs:
The life cycle of bed bugs begins with the hatching of eggs. Female bed bugs can lay up to 500 eggs in their lifetime, which are usually deposited in cracks and crevices near a food source. These eggs are tiny and white, about the size of a pinhead. They hatch in about 5 to 10 days, depending on the temperature and humidity levels.
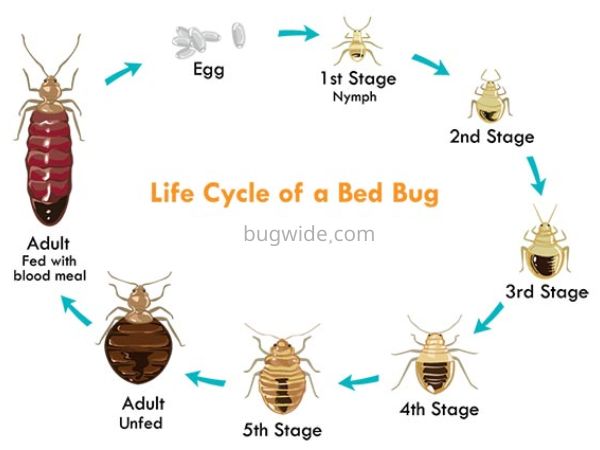
Once the eggs hatch, the bed bug nymphs emerge and immediately begin to feed. Bed bug nymphs go through five stages of molting before reaching adulthood. During each stage, the nymphs molt their exoskeleton and grow larger. This process takes about 5 to 6 weeks, depending on environmental conditions.
After the final molt, the bed bugs are fully grown and sexually mature. They then mate and lay their own eggs, starting the cycle anew.
Mating Habits of Bed Bugs:
How do bed bugs reproduce? Bed bugs mate through a process called traumatic insemination. This is where the male bed bug stabs the female’s abdomen with its reproductive organ, depositing its sperm into her body. This process is not harmful to the female, but it can result in the death of the male if he is not careful.
Once the sperm has been deposited, the female bed bug can lay eggs for the rest of her life. Bed bugs mate every 5 to 10 days, depending on the availability of food.
Laying Eggs:
Female bed bugs lay their eggs in cracks and crevices near a food source. They can lay up to 500 eggs in their lifetime, which are usually deposited in clusters of 10 to 50. The eggs are tiny and white, about the size of a pinhead, and are difficult to see with the naked eye.
Once the eggs are laid, they are difficult to remove. They are usually stuck to the surface with a sticky substance that prevents them from being easily dislodged. This makes it difficult to eliminate bed bugs once they have infested an area.
How do bed bugs grow?
Like all insects, bedbugs have to shed their skin (molt) as they grow. An adult bedbug, for example, molts five times before reaching its full size. Bedbugs must blood meal between each molt. Without a blood meal, bedbugs cannot molt and will die.
Environmental Factors That Affect Bed Bug Reproduction and Growth
Temperature and humidity levels play a significant role in the life cycle of bed bugs. Optimal conditions for bed bugs to reproduce and grow are between 70 and 80°F with relative humidity levels of 70 to 80%.
Under these conditions, bed bugs can complete their life cycle in as little as 4 weeks. In cooler temperatures, bed bugs will slow down their development and may take up to 6 weeks to reach adulthood. In extremely hot or dry conditions, bed bugs will not survive.
Light levels also affect bed bug development. Bed bugs are attracted to light and will hide in dark crevices and cracks during the day. If there is not enough light available, bed bugs may not mate and lay eggs.
What are the consequences of a bed bug infestation?
Bedbugs are mainly active at night and usually hide in bedding or other soft furnishings during the day. A bedbug infestation can cause a number of health and safety concerns, including:
- Anemia (loss of blood)
- Allergic reactions
- Secondary infections from scratching bites
- Asthma attacks in people who are allergic to bedbug bites
- Psychological distress and anxiety
What do bed bugs eat?
While bed bugs will feed on any kind of blood, they prefer human blood. In fact, they are specifically attracted to the CO2 that we exhale. They are able to sense CO2 from up to 20 feet away. This is why you often see them clustered around your head and shoulders in bed – they’re trying to get as close to you as possible to get a meal!
How long do bed bugs live?
Bed bugs can live for about a year without feeding. However, they generally only live for around 6 to 12 months. This is why you may not see bed bugs for a while after you first bring them into your home they’re waiting to mature so they can start reproducing.
How fast do bed bugs reproduce?
A single bed bug can lay up to 500 eggs in its lifetime. Eggs are small, white, and oval-shaped. They are laid singly or in groups and glued to surfaces with a sticky secretion. The average time from egg to adult is about 21 days, although this depends on temperature and other conditions. Under ideal conditions (80°F/26°C and 70-80% humidity), it can take as little as 10 days for a bed bug to mature into an adult.
FAQ’s
No, the one-bed bug cannot reproduce on its own. Bed bugs are social insects and they mate in a process known as traumatic insemination. This process involves a male bed bug using its specialized reproductive organ, called a paramere, to pierce the female’s exoskeleton and deposit sperm directly into her body cavity. This process is not necessary for the female bed bug to lay eggs, but it does increase the likelihood that the eggs will be fertilized.
Bed bugs can reproduce rapidly, with each adult female able to lay between 200 and 500 eggs in her lifetime. The eggs are tiny, white, and almost translucent, making them very difficult to spot. Bed bug eggs typically hatch within 10 days, and the nymphs (young bed bugs) that emerge are pale in color but mature into adults within just a few weeks.
Baby bed bugs, also known as nymphs, are about the size of a poppy seed and are bright white or pale in color. At each molt, nymphs gradually turn darker until they reach maturity. Adult bed bugs are brown in color and large enough to be easily seen by the naked eye. Bed bug eggs are small, white, and oval-shaped.
Wrapping It Up:
Bed bugs are pests that reproduce and grow quickly. Female bed bugs can lay hundreds of eggs, and they require a food source, usually human blood, to sustain their life cycle. Ideal temperature and humidity conditions for reproduction and growth are 70-80°F with 70-80% relative humidity. Preventing and controlling bed bug infestations requires a thorough understanding of their behavior and life cycle, as well as effective prevention methods. Stay informed and vigilant to keep homes free of these pests.

![What Attracts Bed Bugs Most? [5 Things In Homes]](https://lyssfits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/What-Attracts-Bedbugs-Most-Answered-768x484.jpg)

![How To Find Bed Bugs During The Daytime? [Explained]](https://lyssfits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/How-To-Find-Bed-Bugs-During-The-Day-Simple-Guide-768x484.jpg)
![Can Bed Bugs Survive In Cold Weather? [Myth Busted]](https://lyssfits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Can-Bed-Bugs-Survive-In-Cold-Weather-768x484.jpg)

